
Hey Friend!
My name is Trev and I’m the CBD Panda!
I’m so excited to be part of your CBD journey.
Welcome to CBD Panda, a place where you’ll find information and resources to better understand the way our bodies are primed to work with the natural world.
As we evolve, people are increasingly seeking alternatives to the harsh side effects of pharmaceuticals, and looking for health solutions more aligned with our body’s natural processes and how we function on a deep biological level.
Cannabidiol (CBD) is arguably one of the most exciting natural health developments of the modern age. For those new to CBD, it is one of many naturally and non-intoxicating compounds found in the cannabis plant and is abundant in hemp. Following a massive increase in consumer demand, CBD is becoming a global media sensation and is receiving praise from the medical fraternity, celebrities, performance athletes, alternative health advocates and people of all walks of life.
CBD Panda is a team of CBD educators and advocates who dedicate their time to help people cut through the confusion and myths around this wonderful gift from mother nature. We do this by providing information about the human Endocannabinoid System (ECS), regular news and updates, sharing helpful information from reliable sources, and most importantly helping people that reach out to us with questions. We do our best to share information & resources that we’ve found helpful over the years.
Surprising to many, the medicinal use of CBD has a rich history dating back to 2800 B.C. when listed in Chinese Emperor Shen Nung’s pharmacopoeia and used to treat a vast array of health concerns.
Many people that we speak with say they’re confused with the terminology, such as CBD, THC, carrier oil, terpenes, flavonoids, isolate, full-spectrum, broad-spectrum, whole-of-plant, entourage effect, sublingual….. The list goes on and it can all get quite confusing. We also find that sometimes people who legally access CBD through their GP or health professional go online seeking to better understand how CBD works.
We hope our information and resources help to add to your understanding of how it works with your ECS.
The team at CBD Panda began their personal CBD journeys more than 5 years ago! Working with phytocannabinoids to enhance our bodies own Endogenous Cannabinoid System (ECS) has dramatically improved both our health and happiness. Our mission is to fuel the CBD revolution here in Australia. We do this by educating people about this magical gift from sweet mother nature, and in doing so building a community for those devoted to natural wellness.

The rather cute panda that features in all our materials is named Trev, he’s the CBD Panda! Trev promises to do his best to share trusted and true information about all things CBD, and hopefully help you with your own CBD journey.
Much of the information we share is through social media. Check out our Facebook & Instagram pages. You’ll also find blogs and a bunch of other information on this site. So strap yourself in, grab a healthy snack, explore our site and enjoy……
And please if you have any questions, please get in contact with us and we’ll do our best to help.
Our Service
We offer a service as educators to speak at functions and events where people would like to better understand the natural benefits of CBD. Please contact us if you’d like to discuss our range of educational and public speaking services.
IMPORTANT: This website is for educational purposes only. We are not a clinic or doctor referral service. You cannot purchase any CBD products through this website.

The rather cute panda that features in all our materials is named Trev, he’s the CBD Panda! Trev promises to do his best to share trusted and true information about all things CBD, and hopefully help you with your own CBD journey.
Much of the information we share is through social media. Check out our Facebook & Instagram pages. You’ll also find blogs and a bunch of other information on this site. So strap yourself in, grab a healthy snack, explore our site and enjoy……
And please if you have any questions, please get in contact with us and we’ll do our best to help.
Our Service
We offer a service as educators to speak at functions and events where people would like to better understand the natural benefits of CBD. Please contact us if you’d like to discuss our range of educational and public speaking services.
IMPORTANT: This website is for educational purposes only. We are not a clinic or doctor referral service. You cannot purchase any CBD products through this website.

What is CBD?
CBD is one of the hottest holistic wellness topics at the moment. Following a massive increase in consumer demand, CBD is now a global media sensation and is receiving praise from the medical fraternity, celebrities, performance athletes, alternative health advocates and people of all walks of life.
CBD stands for cannabidiol (pronounced Canna-bid-i-ol). Cannabidiol (CBD) is a naturally occurring and non-intoxicating molecule found in the Cannabis Sativa L. plant and is abundant in hemp.
Modern science has isolated and identified 144 different cannabinoids within the cannabis plant. Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is another widely known cannabinoid that is found in the cannabis plant and responsible for the plant’s behavioural and psychotropic effects. There are also many non-psychoactive cannabinoids such as cannabidiol (CBD).
Surprising to many, the medicinal benefits of CBD has a rich history dating back to 2800 B.C. when listed in Chinese Emperor Shen Nung’s pharmacopoeia and used to treat a vast array of health problems. The modern scientific community was slow to catch up, formerly recognising cannabidiol in 1940, just one of at least 144 cannabinoids identified in the Cannabis Sativa plant.
Hemp is the dominant ‘strain’ of the Cannabis Sativa plant used for CBD extraction. This is because the hemp plant has high concentrations of CBD, and is low in THC.
The FDA in the USA classifies ‘industrial hemp’ as containing 0.3% or less THC content by dry weight.
What are Cannabinoids?
Simply put, cannabinoids are natural occurring compounds found in the cannabis plant.
Research has identified 144 different cannabinoids in the cannabis plant, all with differing molecular structures and healing properties. The two main cannabinoids are delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). Other cannabinoids commonly found in full-spectrum CBD oil include THCa, CBDa, CBC, CBG, and CBN.
Endocannabinoids are human-made cannabinoids, being cannabinoids made by our bodies. The two main Endocannabinoids are called Anandamide and 2-AG.
You may also hear the term phytocannabinoid. ‘Phyto’ means plant made, so phytocannabinoids are simply plant made cannabinoids such as CBD.
Cannabinoids interact with our Endocannabinoid System.
How do i use cbd oil?
You will likely receive detailed instructions regarding the use of CBD by your consulting doctor. Here’s some general information to help.
CBD around the world is available in many forms, including oils, edibles, balms, inhalation and a range of other delivery methods. This FAQ refers to the use of CBD oil.
The most common ways to use CBD oil are oral, sublingual and topical methods.
CBD oil orally is simply swallowing the oil. This method is not as effective as the sublingual method.
Sublingual use of CBD oil is the process of placing the oil under your tongue and allowing it sufficient time for the oil to diffuse through the surrounding tissue and into your bloodstream, which differs from regular oral consumption. The desired dose of CBD oil is placed under the tongue and held for at least 90-120 seconds, allowing sufficient time for the oil to diffuse across the epithelial cells. It’s important to note that the oil must be held under the tongue; different areas of the mouth have different types of cells which may not allow diffusion into the bloodstream.
Sublingual application is the most effective way to take CBD oil due to its bioavailability. The term bioavailability refers to how much of a substance can be utilized by the body. Sublingual application of CBD bypasses the metabolic process of digestion, meaning far less of the CBD is lost through digestion. Further, bypassing the slow digestion process means that the effects of CBD can be experienced much faster.
When used topically, a small amount of oil (a number of drops) should be dropped onto the affected area and lightly massaged into the skin. Topical use of CBD is helpful for things like pain, inflammation, sore muscles, headaches, tick bites, and skin conditions like acne.
What is the endocannabinoid system (ecs)?
Your Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is an internal system critical for almost every aspect of our moment-to-moment functioning. The human ECS is a vast internal biological system made up of chemical signals (endocannabinoids, being cannabinoids produced by our bodies) and cell receptors densely packed throughout our brains and bodies. Together these help regulate and maintain homeostasis (or balance) within your body.
Every living human body naturally produces molecules called endocannabinoids, similar to CBD. One is called Anandamide and is believed to be responsible for the ‘runner’s high’. The scientific community named the molecule “Anandamide” which is Sanskrit for bliss, a word suggestive of its mood-altering effects.
Endocannabinoids interact with cannabinoid cell receptors in your ECS, the two main types being:
- CB1 Receptors: located in the brain and central nervous system, in particular the midbrain and spinal cord regions that are responsible for pain perception; and
- CB2 Receptors: located in the peripheral nervous system (including immune cells).
Harvard Medical School reports that the “cannabinoid” receptors in the brain — the CB1 receptors — outnumber many of the other receptor types on the brain.
So how does this system work? Endocannabinoids and phytocannabinoids such as CBD bind to the CB1 and CB2 cell receptors in the body and match up like a lock & key. When this happens, it is believed that they stimulate the cell receptor signalling that the ECS needs to take action, modulating things like pain, inflammation, mood, movement and sleep.
CBD is a phyto-cannabinoid, meaning plant-made. CBD, much like our human-made cannabinoids, activates the ECS and helps get your body back into balance, or homeostasis as it’s called.
Full-Spectrum, Broad-Spectrum and CBD Isolate Explained
There are three main types of CBD oil that you might hear about, including full-spectrum broad-spectrum, CBD Isolate.
The difference between full-spectrum broad-spectrum, CBD isolate is largely the cannabinoid content found in each of the products. Modern science has isolated and identified 144 different cannabinoids within the cannabis plant.
Full-spectrum CBD oil contains all of the cannabinoids (including THC) and other plant compounds that can be extracted from the plant, including terpenes, flavonoids, proteins, fibre and a host of essential vitamins, fatty acids, and minerals. The extraction process used with full-spectrum CBD is designed so that none of the cannabinoids and other compounds of the plant have been removed. Full spectrum CBD does contain THC (the cannabinoid best known for getting people high), however there are only trace elements of THC in full-spectrum CBD oil, not enough THC to get you high.
Broad-spectrum CBD also contains most of the cannabinoids and other plant compounds, however broad-spectrum CBD goes through an additional process to remove the THC.
CBD isolate is precisely what the name implies: the purest form of CBD.
The process to obtain CBD isolate follows the same route as full-spectrum CBD, with the addition of some extra processing steps in order to isolate CBD from the rest of the plant extracts.
What is the Entourage Effect?
Simply put, The Entourage Effect is the theory that all compounds in cannabis (such as cannabinoids, terpenes and flavonoids) work synergistically together, and the interaction between all of the compounds come together to produce a better effect than when taken alone.
The term ‘entourage effect’ came into existence in the 1990s by a group of Israeli researchers that were pivotal in research into the human Endocannabinoid System and how cannabinoids enhance and complement each other.
Each individual component of the cannabis plant has its own healing properties. When combined, the components of the plant have a greater effect when working together compared with each individual component alone.
Think about a sports team. Each player may have great skills as an individual and their talent can operate in isolation. However an individual player can have an entirely different impact when combined with other players in the team.

What is CBD?
CBD is one of the hottest holistic wellness topics at the moment. Following a massive increase in consumer demand, CBD is now a global media sensation and is receiving praise from the medical fraternity, celebrities, performance athletes, alternative health advocates and people of all walks of life.
CBD stands for cannabidiol (pronounced Canna-bid-i-ol). Cannabidiol (CBD) is a naturally occurring and non-intoxicating molecule found in the Cannabis Sativa L. plant and is abundant in hemp.
Modern science has isolated and identified 144 different cannabinoids within the cannabis plant. Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is another widely known cannabinoid that is found in the cannabis plant and responsible for the plant’s behavioural and psychotropic effects. There are also many non-psychoactive cannabinoids such as cannabidiol (CBD).
Surprising to many, the medicinal benefits of CBD has a rich history dating back to 2800 B.C. when listed in Chinese Emperor Shen Nung’s pharmacopoeia and used to treat a vast array of health problems. The modern scientific community was slow to catch up, formerly recognising cannabidiol in 1940, just one of at least 144 cannabinoids identified in the Cannabis Sativa plant.
Hemp is the dominant ‘strain’ of the Cannabis Sativa plant used for CBD extraction. This is because the hemp plant has high concentrations of CBD, and is low in THC.
The FDA in the USA classifies ‘industrial hemp’ as containing 0.3% or less THC content by dry weight.
CBD stands for cannabidiol (pronounced Canna-bid-i-ol). Cannabidiol (CBD) is a naturally occurring and non-intoxicating molecule found in the Cannabis Sativa L. plant and is abundant in hemp.
Modern science has isolated and identified 144 different cannabinoids within the cannabis plant. Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is another widely known cannadioid that is found in the cannabis plant and responsible for the plant’s behavioural and psychotropic effects. There are also many non-psychoactive cannabinoids such as cannabidiol (CBD).
Surprising to many, the medicinal benefits of CBD has a rich history dating back to 2800 B.C. when listed in Chinese Emperor Shen Nung’s pharmacopoeia and used to treat a vast array of health problems. The modern scientific community was slow to catch up, formerly recognising cannabidiol in 1940, just one of at least 144 cannabinoids identified in the Cannabis Sativa plant.
Hemp is the dominant ‘strain’ of the Cannabis Sativa plant used for CBD extraction. This is because the hemp plant has high concentrations of CBD, and is low in THC.
The FDA in the USA classifies ‘industrial hemp’ as containing 0.3% or less THC content by dry weight.
What are cannabinoids?
Simply put, cannabinoids are natural occurring compounds found in the cannabis plant.
Research has identified 144 different cannabinoids in the cannabis plant, all with differing molecular structures and healing properties. The two main cannabinoids are delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). Other cannabinoids commonly found in full-spectrum CBD oil include THCa, CBDa, CBC, CBG, and CBN.
Endocannabinoids are human-made cannabinoids, being cannabinoids made by our bodies. The two main Endocannabinoids are called Anandamide and 2-AG.
You may also hear the term phytocannabinoid. ‘Phyto’ means plant made, so phytocannabinoids are simply plant made cannabinoids such as CBD.
Cannabinoids interact with our Endocannabinoid System.
How do I use CBD oil?
You will likely receive detailed instructions regarding the use of CBD by your consulting doctor. Here’s some general information to help.
CBD around the world is available in many forms, including oils, edibles, balms, inhalation and a range of other delivery methods. This FAQ refers to the use of CBD oil.
The most common ways to use CBD oil are oral, sublingual and topical methods.
CBD oil orally is simply swallowing the oil. This method is not as effective as the sublingual method.
Sublingual use of CBD oil is the process of placing the oil under your tongue and allowing it sufficient time for the oil to diffuse through the surrounding tissue and into your bloodstream, which differs from regular oral consumption. The desired dose of CBD oil is placed under the tongue and held for at least 90-120 seconds, allowing sufficient time for the oil to diffuse across the epithelial cells. It’s important to note that the oil must be held under the tongue; different areas of the mouth have different types of cells which may not allow diffusion into the bloodstream.
Sublingual application is the most effective way to take CBD oil due to its bioavailability. The term bioavailability refers to how much of a substance can be utilized by the body. Sublingual application of CBD bypasses the metabolic process of digestion, meaning far less of the CBD is lost through digestion. Further, bypassing the slow digestion process means that the effects of CBD can be experienced much faster.
When used topically, a small amount of oil (a number of drops) should be dropped onto the affected area and lightly massaged into the skin. Topical use of CBD is helpful for things like pain, inflammation, sore muscles, headaches, tick bites, and skin conditions like acne.
What is the endocannabinoid system (ecs)?
Your Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is an internal system critical for almost every aspect of our moment-to-moment functioning. The human ECS is a vast internal biological system made up of chemical signals (endocannabinoids, being cannabinoids produced by our bodies) and cell receptors densely packed throughout our brains and bodies. Together these help regulate and maintain homeostasis (or balance) within your body.
Every living human body naturally produces molecules called endocannabinoids, similar to CBD. One is called Anandamide and is believed to be responsible for the ‘runner’s high’. The scientific community named the molecule “Anandamide” which is Sanskrit for bliss, a word suggestive of its mood-altering effects.
Endocannabinoids interact with cannabinoid cell receptors in your ECS, the two main types being:
- CB1 Receptors: located in the brain and central nervous system, in particular the midbrain and spinal cord regions that are responsible for pain perception; and
- CB2 Receptors: located in the peripheral nervous system (including immune cells).
Harvard Medical School reports that the “cannabinoid” receptors in the brain — the CB1 receptors — outnumber many of the other receptor types on the brain.
So how does this system work? Endocannabinoids and phytocannabinoids such as CBD bind to the CB1 and CB2 cell receptors in the body and match up like a lock & key. When this happens, it is believed that they stimulate the cell receptor signalling that the ECS needs to take action, modulating things like pain, inflammation, mood, movement and sleep.
CBD is a phyto-cannabinoid, meaning plant-made. CBD, much like our human-made cannabinoids, activates the ECS and helps get your body back into balance, or homeostasis as it’s called.
Full-Spectrum, Broad-Spectrum and CBD Isolate Explained
There are three main types of CBD oil that you might hear about, including full-spectrum broad-spectrum, CBD Isolate.
The difference between full-spectrum broad-spectrum, CBD isolate is largely the cannabinoid content found in each of the products. Modern science has isolated and identified 144 different cannabinoids within the cannabis plant.
Full-spectrum CBD oil contains all of the cannabinoids (including THC) and other plant compounds that can be extracted from the plant, including terpenes, flavonoids, proteins, fibre and a host of essential vitamins, fatty acids, and minerals. The extraction process used with full-spectrum CBD is designed so that none of the cannabinoids and other compounds of the plant have been removed. Full spectrum CBD does contain THC (the cannabinoid best known for getting people high), however there are only trace elements of THC in full-spectrum CBD oil, not enough THC to get you high.
Broad-spectrum CBD also contains most of the cannabinoids and other plant compounds, however broad-spectrum CBD goes through an additional process to remove the THC.
CBD isolate is precisely what the name implies: the purest form of CBD.
The process to obtain CBD isolate follows the same route as full-spectrum CBD, with the addition of some extra processing steps in order to isolate CBD from the rest of the plant extracts.
What is the Entourage Effect?
Simply put, The Entourage Effect is the theory that all compounds in cannabis (such as cannabinoids, terpenes and flavonoids) work synergistically together, and the interaction between all of the compounds come together to produce a better effect than when taken alone.
The term ‘entourage effect’ came into existence in the 1990s by a group of Israeli researchers that were pivotal in research into the human Endocannabinoid System and how cannabinoids enhance and complement each other.
Each individual component of the cannabis plant has its own healing properties. When combined, the components of the plant have a greater effect when working together compared with each individual component alone.
Think about a sports team. Each player may have great skills as an individual and their talent can operate in isolation. However an individual player can have an entirely different impact when combined with other players in the team.
FROM THE BLOG
How to Calculate CBD Dose
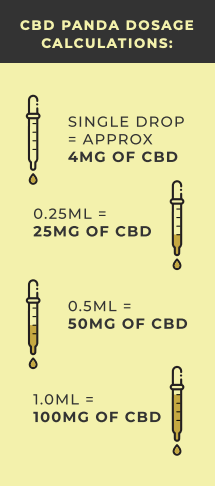
To determine an exact dose of CBD, we need to start with the dropper. Always remember that each FULL dropper of oil equals 1mL of fluid. This means that a 30mL bottle of CBD oil will have roughly 30 FULL droppers.
CBD Panda contains 100mg of CBD per 1ml of oil. So for each full dropper you get 100mg of full-spectrum CBD.
Where possible, we try to provide a relevant frame of reference. In terms of potency, we understand that at the time of writing, the highest prescribed CBD oil available under the government scheme is 140mg/ml.
CBD Panda is at the potent end of the CBD spectrum, it’s the good stuff!
There are no official recommended dosages. If a doctor or specialist hasn’t provided you with a recommendation, it’s best to start with a smaller dosage and gradually increase it. This could mean starting with 25mg to 50mg of CBD per day for a week or two and then adjusting as needed. If you’re keen to try CBD yet prefer a cautious approach, start with one or two drops a day for a week, then increase until your symptoms change.
As a general guide for moderate symptoms, a range of 0.5mg – 1.0mg of CBD per kilogram of body weight per day is suggested. So for example, if a person weighing 80 kgs is suffering moderate insomnia and is looking to try CBD, a daily dose of between 40mg and 80mg of CBD is a reasonable place to start and then adjust accordingly. In this example, it would seem sensible to start at 50mg of CBD (half a dropper of oil) each day for a week and then adjust accordingly.
Looking for additional dosage Information? To assist you in finding the right application of CBD for you, here is a selection of reputable third-party (non-corporate) educational videos.
Regardless, there are a variety of differing CBD usage practices available and unfortunately a myriad of inconsistent & unreliable information out there. To this end, our team has sourced the above videos to ensure that our friends have access to a range of trustworthy information. We further trust that you will always make informed choices when it comes to your own health and wellbeing.
READ THE FAQ's

OUR RESPECTS
We pay our respects to the First Nations People of Australia and acknowledge the Kombumerri people of the Yugambeh Language group, on which lands we live, work and play. We acknowledge that sovereignty was never ceded and honour their elders – past, present & emerging.
Contact Us
PO Box 563
Miami QLD 4220
Yugambeh Land
Trev loves a good chat and is happy to answer any questions you have to the best of his ability! Click the link below to send Trev a message…
Talk to Trev!
The content and information presented on www.cbdpanda.com.au is strictly provided for educational purposes.
ALL CONTENT PROVIDED WAS WRITTEN BY THE TEAM AT CBD PANDA AND REPRESENTS THE AUTHOR’S OPINION. ALL INFORMATION PRESENTED IS BASED ON RELIABLE SOURCES. THE TEAM AT CBD PANDA ARE NOT DOCTORS OR MEDICAL PROFESSIONS, AND ARE NOT OFFERING MEDICAL ADVICE. NO INFORMATION PRESENTED IS INTENDED TO DIAGNOSE, TREAT, CURE OR PREVENT ANY DISEASE. WE DO NOT RECOMMEND ANY PARTICULAR CBD PRODUCT. YOU CANNOT PURCHASE ANY CBD PRODUCTS THROUGH THIS WEBSITE. IT IS STRONGLY RECOMMENDED THAT YOU CONSULT YOUR GP/DOCTOR OR OTHER HEALTH PROFESSIONAL IN RELATION TO CBD.




